Movement data
Across the U.S. swine industry, animals and other products (such as semen and germplasm) are transported between farms and states. RABapp™utilize such data to build detailed, transportation networks Figure 1 for contact tracing, risk calculations, and outbreak simulations.
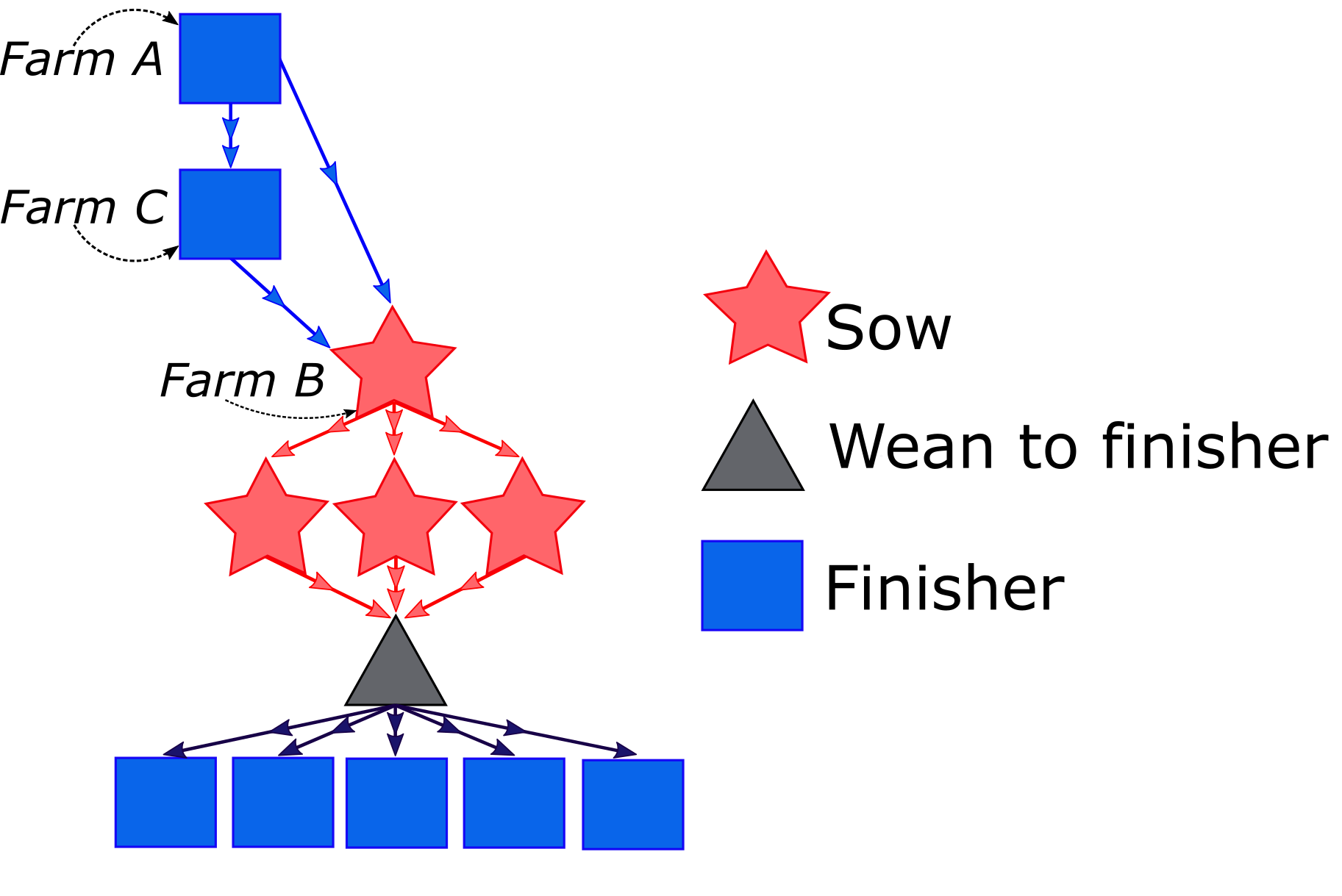
Farm type classification
The RABapp™ follow the US SHIP farm type classification. See table below.
| Farm type | Description |
|---|---|
| Boar Stud | Production site with mature boars (inventory) that distribute semen to other production sites. (e.g. boar stud, with or without on-site isolation). |
| Breeding Herd | Production site with breeding females and house >= 1,000 breeder or feeder swine. (e.g. breed-to-wean, breeding/gestation or farrowing only, with or without on-site gilt isolation/grow-out). |
| Growing Pig | Production site with >= 1,000 feeder swine (nursery, grower, or finisher). |
| Farrow to Feeder or Farrow to Finish | Production site with breeding females, grow feeder swine for purposes other than breeding stock replacement for this particular farm site, and house >=1,000 breeder or feeder swine. |
| Small Holding | Production sites with >= 100 and < 1,000 breeder or feeder swine. |
| Non-commercial | Production sites with < 100 breeder or feeder swine. |
| Live animal marketing operations | A dealer with a livestock yard/buying station (facility) that markets > 100 swine / week for resale of such swine to slaughter facilities. |